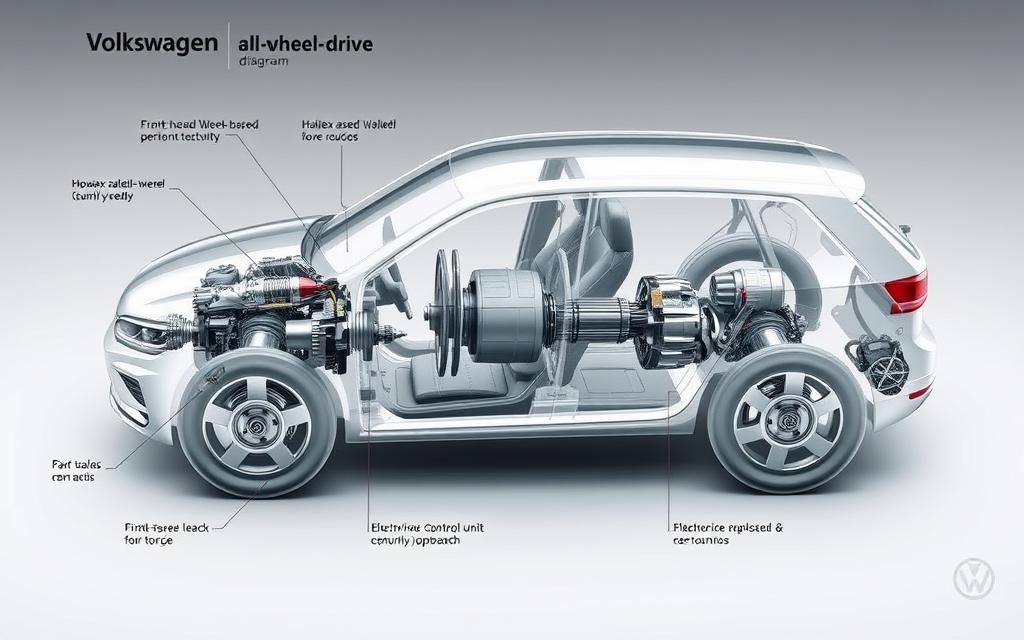
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION technology is a top-notch way to keep vehicles stable and in control. It started as Syncro in the 1980s and has grown into a smart all-wheel drive (AWD) system. It sends power to the right wheels to keep traction strong.
The system works in two ways, depending on the engine’s position. Engines in the front use Haldex couplings for better front-wheel drive. Engines in the back use Torsen differentials for better rear-wheel drive. This lets Volkswagen make different cars for different needs.
When comparing Volkswagen’s 4MOTION to Audi’s quattro, we see some big differences. Both are safe, but 4MOTION reacts faster in city driving. The latest versions can even predict when a wheel might slip, helping drivers in changing weather.
Volkswagen keeps improving 4MOTION to make it a great choice for many drivers. It’s good for both daily driving and rough terrain. That’s why 4MOTION is a favourite in the AWD market.
Understanding Volkswagen’s 4MOTION Technology
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION all-wheel drive system is a blend of mechanical and electronic engineering. It adapts to driving conditions by adjusting torque between axles. This approach has evolved a lot over time.
Core principles of all-wheel drive systems
Modern AWD systems, like 4MOTION, aim to send power where it’s most needed. They differ from permanent 4WD by using sensors to detect wheel slip quickly. The Haldex coupling then sends up to 50% of engine torque to the rear axle when needed.
Historical development by Volkswagen
Volkswagen started with the 1980s Syncro system in the T3 Transporter. This used viscous couplings, unlike today’s electronic controls. The real leap forward was in 1998 with the introduction of 4MOTION in fourth-generation Golf models.
From Syncro to modern implementations
The move from Syncro to 4MOTION brought Volkswagen to use electronic control units. Early systems were mechanical, but now MQB-platform vehicles use predictive algorithms. This change allows for torque distribution before wheel slip happens.
Key engineering milestones
Two key developments shaped 4MOTION:
- 2016’s fifth-generation Haldex coupling with faster response
- Adding Torsen differentials in performance models like the Golf R
These changes turned 4MOTION into a dynamic handling tool. It now works well with ESC and XDS+ electronic differentials. This creates “torque vectoring by brake”.
How 4MOTION Works: Technical Breakdown
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION system changes how cars drive by adapting quickly to the road. It makes decisions in just milliseconds. This part looks at the amazing tech behind these fast choices.

Haldex Coupling System Fundamentals
The fifth-generation Haldex coupling is a big step forward in AWD tech. It’s not like old mechanical systems. This new unit uses 15 sensors to check:
- Wheel rotation speeds
- Steering angles
- Throttle positions
- G-force measurements
Fifth-Generation Component Architecture
Haldex Gen5 is 40% quicker than before. It can send up to 50% of torque to the rear axle before wheels slip. It has new features like:
- An integrated pump motor for exact pressure control
- Lighter aluminium housing
- Self-learning software that gets better with use
Electronic Differential Lock Functionality
On rough ground, the EDL braking system is key. It uses brakes to control power:
- Applies individual wheel braking
- Redirects power to wheels with grip
- Works well with ABS
In the Volkswagen Tiguan, EDL can send 100% of torque to one wheel off-road. It kicks in in just 0.25 seconds if a wheel loses traction.
Interaction With ESC and Traction Control
The Vehicle Dynamics Manager is the system’s brain. It controls:
- 4MOTION torque distribution
- Electronic Stability Control actions
- XDS+ electronic differential functions
This teamwork helps make sharp turns. For example, in the Touareg, it subtly brakes inner wheels and boosts rear axle torque. This makes turns feel tighter.
Key Benefits of 4MOTION AWD
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION system offers more than just all-weather driving. It smartly splits power and improves how cars handle tough roads and fast driving.
Enhanced Traction in Adverse Conditions
The Snow Mode in Tiguan and Atlas models shows its worth in winter. It tweaks how the car responds to the throttle and gears to stop wheelspin on ice. This makes the car go faster by up to 19% than cars without 4MOTION in tests.
Performance on Snow and Wet Surfaces
Tests show 4MOTION cars keep 83% of their grip on snowy roads, 22% more than cars with just front wheels. The electronic differential lock is great at stopping the car from sliding on wet roads, moving power fast to stop slipping.
Improved Vehicle Dynamics During Cornering
Tests at the Nürburgring show 4MOTION cars corner 4% faster than cars with rear wheels. It uses data from the steering and how the car moves 200 times a second. This helps it send power to the right wheels before the car starts to slip.
Weight Distribution Advantages
In the ID.4 GTX, the AWD parts are placed low in the car. This makes the car more stable, with a 48:52 front-rear weight balance. It also lowers the car’s centre of gravity by 15mm, making it better in emergency stops.
| Feature | 4MOTION Advantage | Standard AWD Comparison |
|---|---|---|
| Snow Acceleration | 0-60 mph in 8.2s | 9.8s average |
| Wet Surface Braking | 34.1m (70-0 mph) | 38.6m average |
| Cornering G-Force | 0.87g | 0.79g average |
Volkswagen’s team calls this system “predictive traction management”. It’s designed to prevent slipping, not just react to it.
Volkswagen Models Featuring 4MOTION
Volkswagen uses 4MOTION all-wheel-drive technology in many vehicles. It makes each car better for its job, whether it’s an SUV or an electric car. The system helps with traction and handling.

SUV Applications: Tiguan and Touareg
The Tiguan and Touareg are great for off-road adventures. They have a special system for different terrains. The Tayron can even tow up to 2.5 tonnes, a record in its class.
Terrain Response Capabilities
Drivers can choose from various driving modes. This includes:
- Snow mode for slippery surfaces
- Off-road setting for steep hills
- Custom mode for mixed conditions
Performance Vehicles: Golf R and Arteon
In the Golf R, 4MOTION helps with cornering. The Arteon focuses on high-speed stability. The Golf R also has Drift Mode for fun on the track.
Electric Adaptation in ID.4 GTX
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION AWD system is updated for electric cars like the ID.4 GTX. It has two electric motors for quick torque adjustments. Key specs include:
| Model | Power Output | Torque Split Range | Unique Feature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tiguan | 187 PS | 50:50 (front:rear) | Hill Descent Control |
| ID.4 GTX | 299 PS | 0-100% (variable) | Regenerative Braking Integration |
| Golf R | 315 PS | 50:50 (default) | Drift Mode |
This table shows how Volkswagen customises 4MOTION for different cars. The ID.4 GTX benefits from fast electric torque, making it better than traditional AWD systems.
4MOTION vs Competitor AWD Systems
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION stands out in all-wheel drive technology. It’s unique engineering makes it different from Audi’s Quattro ultra, Subaru’s Symmetrical AWD, and BMW’s xDrive.
Comparison with Audi Quattro Ultra
4MOTION uses a transverse engine layout. This is different from Audi’s Quattro system, which has a longitudinal layout. The Haldex coupling in 4MOTION allows for quicker torque transfer to the rear wheels than Quattro’s Torsen differential.
Torque Distribution Strategies
Both systems mainly use the front wheels for normal driving. But, 4MOTION can send up to 50% of the torque to the rear wheels in milliseconds. Quattro ultra, on the other hand, distributes torque more slowly, focusing on stability in slippery conditions.
Contrast with Subaru Symmetrical AWD
Subaru’s Symmetrical AWD is a permanent system. It’s different from Volkswagen’s on-demand 4MOTION. Subaru’s system has equal-length drive shafts and always sends power to all wheels. 4MOTION only engages the rear wheels when it senses slippage.
Mechanical vs Electronic Solutions
The design difference affects fuel efficiency and performance. Subaru’s system is good for off-road driving because it’s predictable. But, 4MOTION’s electronic control is better for city driving, saving fuel.
BMW xDrive System Differences
BMW’s xDrive system is designed for sporty driving. It sends more power to the rear wheels during sharp turns. This is different from 4MOTION, which balances power between the front and rear wheels.
| Feature | 4MOTION | Quattro Ultra | Symmetrical AWD | xDrive |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Torque Distribution | Up to 50% rear | Up to 85% rear | Fixed 60:40 split | Up to 100% rear |
| System Type | On-demand | Full-time | Full-time | Active |
| Primary Use Case | Urban/light off-road | Performance driving | Off-road stability | Dynamic handling |
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION is designed to be versatile. It balances everyday use with off-road capability. While others are better in certain areas, 4MOTION offers a good balance for drivers who want flexibility.
Maintenance and Ownership Considerations
Having a Volkswagen with 4MOTION is great, but keeping it in top shape is key. Regular maintenance keeps it running smoothly and saves you money in the long run.

Recommended Service Intervals
Volkswagen says to service the Haldex system every 60,000 miles. This includes:
- Full pump filter cleaning
- Haldex coupling inspection
- Software updates for torque distribution logic
Fluid Change Requirements
Haldex fluid should be replaced every 60k miles. But, differential oils need a change every 30,000 miles if you drive a lot. Experts say:
“Using VW-approved fluids prevents viscosity breakdown that can lead to premature clutch wear.”
Common Maintenance Challenges
Watch out for:
- Clutch plate degradation in stop-and-go traffic
- Corrosion in electrical connectors from road salt
- ESC sensor malfunctions affecting torque distribution
Look out for shuddering in low-speed turns or AWD warning lights. Fixing these issues early stops bigger problems.
Optimising System Longevity
Three ways to make 4MOTION last longer:
- Avoid prolonged deep water exposure to protect electronic components
- Perform annual undercarriage inspections for debris accumulation
- Use OEM-specification parts during repairs
Dealers suggest bi-annual system checks, even when not due for a service. This is important for vehicles in harsh climates.
Conclusion
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION system shows how car tech evolves. It started with mechanical differentials and now has electric torque distribution in the ID.4 GTX. This tech stays relevant thanks to smart engineering.
The electric version of 4MOTION is really interesting. It uses two motors for quick power shifts, without the need for old-school parts.
Looking ahead, AWD tech will likely get even better. Volkswagen is leading the way by mixing old-school stability with new EV precision. The ID.4 GTX is a great example, with its rear power system for better handling and less energy use.
Compared to Audi’s Quattro ultra or BMW xDrive, 4MOTION is unique. It works well with different types of engines. This makes Volkswagen ready for any market need, from gas SUVs to fast EVs.
Maintenance for these cars is also getting easier. Electric cars have less to fix, but they’re just as good in all weather.
Volkswagen’s focus on both new ideas and real-world use makes 4MOTION a top choice. As cars change, this system keeps drivers connected to the road and the planet.
FAQ
What distinguishes Volkswagen’s 4MOTION from other AWD systems?
Volkswagen’s 4MOTION is a top-tier all-wheel-drive system. It works differently for cars with engines in the front or back. It started with the Syncro in 1985 and now uses the latest Haldex technology for quick torque shifts.
How does the latest Haldex system improve upon previous 4MOTION implementations?
The new Gen5 Haldex system uses an electrohydraulic coupling. It gets ready for torque shifts before wheels slip. This makes the car grip better and faster, even on sudden turns or slippery surfaces.
Can 4MOTION function with fully electric vehicles?
Yes, the ID.4 GTX shows 4MOTION works with electric cars. It uses separate motors for the front and back axles. This lets it send power quickly and smoothly, keeping the car stable and balanced.
What maintenance does the Haldex system require?
Volkswagen suggests checking the Haldex system every 3 years or 30,000 miles. This includes changing the filter and oil. Drivers should watch for wear on the clutch plates, mainly in city driving. Also, keep the pump strainer clean to avoid problems.
How does 4MOTION compare to Subaru’s Symmetrical AWD system?
Subaru’s system always sends power to all wheels, while 4MOTION mostly drives the front wheels. Subaru’s system splits power evenly, but 4MOTION can disconnect the rear axle for better fuel efficiency.
What advanced features utilise 4MOTION’s capabilities in current models?
The Touareg and Tayron use 4MOTION for off-road driving. They have hill descent control and adjust power for better traction. The Golf R has a Drift Mode that sends more power to the rear wheels for fun driving.
How does 4MOTION integrate with modern driver assistance systems?
In cars like the Tiguan and Touareg, 4MOTION works with Lane Assist and Travel Assist. It adjusts power to help with steering, keeping the car stable. This is very useful in wet conditions.
What weight distribution advantages does 4MOTION offer?
The MQB platform puts the Haldex coupling ahead of the rear axle. This gives models like the Arteon R a near 50:50 weight balance. The ID.4 GTX has floor-mounted batteries for even better balance, reaching 0.72g in Nürburgring tests.