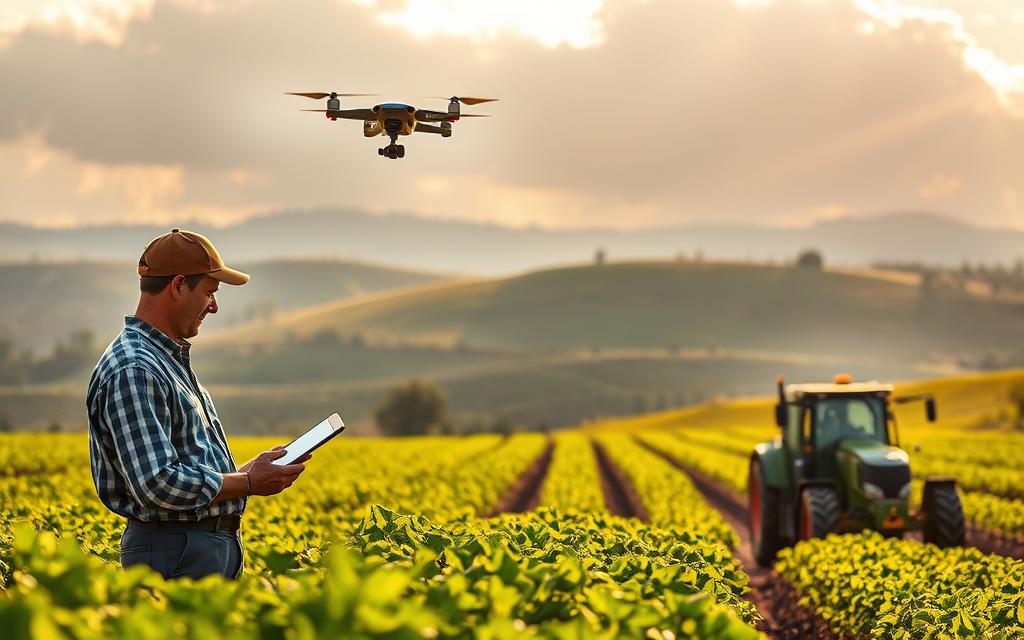
Agriculture has long been guided by nature’s cadence, wisdom of elders, and seasonal patterns. The advent of technology has brought significant changes to this traditional practice.
For many farmers, the question is no longer whether to adopt tech tools, but how to do so without losing their identity and ancestral knowledge. Traditional farming is not outdated; it’s time-tested.
This guide explores the thoughtful adoption of technological tools in agriculture, preserving valuable traditional knowledge while addressing modern challenges.
The Evolution of Farming: Tradition Meets Technology
The agricultural landscape is undergoing a significant transformation as traditional farming methods intersect with modern technology. Contrary to stereotypes, many traditional farmers aren’t anti-tech; they’re anti-disruption, often due to past experiences with failed projects or tools that didn’t translate culturally or literally.
- Generational knowledge and sustainable practices
- Cultural heritage and community knowledge systems
- Adaptations specific to local environments
Core Values of Traditional Farming
Traditional farming systems embody deep ecological understanding and sustainable resource management. These practices represent more than just techniques; they encompass cultural heritage and community knowledge. The knowledge passed down through generations remains relevant today.
The Impact of Technology on Modern Agriculture
Modern agricultural technology offers capabilities for monitoring, analysis, and precision, addressing challenges like climate change and resource scarcity. The intersection of traditional wisdom and tech creates opportunities for more resilient and productive agriculture. Successful integration respects farmers’ existing knowledge while introducing complementary technology.
Benefits of Integrating Technology with Traditional Farming
Integrating technology into farming practices can lead to improved productivity and sustainability. By leveraging modern tools and techniques, farmers can enhance their operations and achieve better outcomes.
Increased Productivity and Yields
Technology integration can significantly boost farm productivity through more precise resource application and timely interventions. Research indicates potential yield increases of 30-70%, benefiting farmers worldwide.
Resource Optimization and Sustainability
Modern agriculture tools enable farmers to optimize inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides, reducing waste while maintaining or improving output quality. This leads to more sustainable farming practices and better soil health management.
Economic Advantages for Farmers
The economic benefits of technology integration in farming include higher yields, reduced input costs, access to premium markets, and improved negotiating power for farmers. This contributes to a more viable and profitable agriculture sector.
Assessing Your Farm’s Technology Needs
To maximize the benefits of technology in farming, understanding your farm’s unique challenges is essential. Assessing your farm’s technology needs involves a thorough evaluation of your current operations and identifying areas where technology can make a significant impact.

Key Challenges and Opportunities
Identifying key challenges and opportunities is crucial in determining the right technologies for your farm. This involves analyzing factors such as labor constraints, resource inefficiencies, and market access limitations. By understanding these challenges, farmers can prioritize technologies that address their most pressing needs.
- Conduct a thorough assessment of operational challenges, considering labor, resources, and market access.
- Identify areas where technology can improve efficiency and productivity.
- Involve all stakeholders, including family members and farm workers, in the assessment process.
Setting Clear Goals
Setting clear goals for technology integration is vital for successful adoption. Farmers should define specific objectives that address their identified challenges, rather than adopting technology for its own sake. This involves considering both immediate needs and long-term objectives when evaluating potential technological solutions.
By setting clear goals, farmers can ensure that the technologies they adopt provide a reasonable return on investment and address their most pressing challenges. Effective goal-setting also helps in prioritizing technologies that are user-friendly and offer adequate support.
When selecting technologies, it’s crucial to consider the level of customer support provided, including training options such as on-farm training or remote workshops, and the quality of after-sales support. This ensures that farmers can maximize the benefits of their chosen technologies.
Essential Technologies for Traditional Farms
Farmers are increasingly adopting innovative technologies to improve crop yields and reduce waste. This shift towards technology integration is transforming traditional farming practices.
IoT Devices and Smart Sensors
Affordable IoT devices measure soil moisture, pH levels, and nutrient content, enabling real-time monitoring. For instance, India’s e-Choupal initiative used internet kiosks with sensor feedback to adjust irrigation.

Mobile Applications and Farm Management Software
Mobile apps provide crop management guidance, pest alerts, and best practices. Farm management software centralizes data, supporting better decision-making.

Weather Stations and Monitoring Tools
Weather stations help farmers make informed decisions about planting, irrigation, and harvest timing based on local conditions.

The key technologies include IoT devices, mobile applications, and weather stations, which offer significant benefits with relatively low investment and technical expertise.
- IoT devices and smart sensors monitor critical factors like soil moisture and temperature.
- Mobile applications provide accessible technology adoption, offering weather forecasts and pest identification.
- Weather stations enable informed decisions on planting and irrigation.
- Farm management software centralizes data for better decision-making.
Precision Agriculture Techniques for Small-Scale Farms
By adopting precision agriculture techniques, small-scale farmers can improve crop yields, reduce waste, and promote sustainable farming practices. These techniques allow for site-specific crop management, resource optimization, and yield monitoring, making farming operations more efficient.
Soil Monitoring and Analysis
Soil monitoring and analysis technologies provide detailed insights into soil health, nutrient levels, and moisture content. This information enables farmers to make informed decisions about amendments and crop selection, ultimately improving soil fertility and crop productivity.
Precision Irrigation Systems
Precision irrigation systems deliver water exactly where and when crops need it, reducing waste while improving plant health and yield potential. This targeted approach to irrigation helps conserve water resources and minimizes the environmental impact of farming operations.
Targeted Application of Inputs
The targeted application of inputs like fertilizers and pesticides minimizes waste, reduces environmental impact, and optimizes the economic return on these investments. By using precision farming tools, farmers can apply inputs only where necessary, reducing the overall cost and environmental footprint of their farming operations.
| Technique | Benefits | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Soil Monitoring | Improved soil health, informed crop selection | Increased crop productivity |
| Precision Irrigation | Water conservation, reduced waste | Improved plant health, yield potential |
| Targeted Inputs | Reduced waste, optimized economic return | Minimized environmental impact |
Advanced Technologies Worth Considering
Advanced technologies are transforming the agricultural landscape, offering new opportunities for farmers worldwide. These innovations are not only improving productivity but also enhancing sustainability and efficiency.
Drones for Field Mapping and Monitoring
Drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and sensors are revolutionizing farm management. They enable precision agriculture by providing detailed field mapping and real-time crop monitoring.
AI and Machine Learning Applications
Machine learning models are being used to predict crop diseases before symptoms appear, allowing for timely interventions. However, the success of these models depends on the quality of local data, highlighting the need for robust datasets.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is being adopted to ensure supply chain transparency and product authenticity. This technology helps farmers secure better pricing and accountability by certifying the origin and quality of their produce.
These advanced technologies are becoming increasingly accessible to smaller farms through service providers and cooperatives, enabling them to benefit from tech innovations.
How to Integrate Technology with Traditional Farming: A Step-by-Step Approach
Integrating technology with traditional farming practices requires a thoughtful and multi-step approach. This process involves careful planning, gradual implementation, and continuous evaluation to ensure successful technology adoption.
Step1: Research and Planning
The first step in integrating technology is to assess current farming operations and identify areas for improvement. This involves evaluating resource availability and defining specific needs. Thorough research into available technological solutions is crucial, considering factors like cost-effectiveness and implementation requirements.
Step2: Start Small with Pilot Projects
Starting with small pilot projects allows farmers to test new technologies with minimal risk. This approach enables them to gain experience and build confidence before wider implementation. Monitoring results closely is essential during this phase.
Step3: Evaluate Results and Scale Up
Careful evaluation of pilot results is necessary, examining both quantitative metrics (such as yield and resource use) and qualitative factors (like ease of use and worker satisfaction). Successful technologies can then be scaled up incrementally, with continuous refinement of processes and adequate training for all users.

Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Adopting technology in traditional farming requires overcoming various hurdles. Farmers face numerous challenges when integrating technology into their practices, ranging from digital literacy gaps to connectivity issues.
Addressing Digital Literacy Gaps
Digital literacy represents a significant barrier for many farmers, particularly older generations or those in regions with limited technology exposure. Effective digital skills training programs can help bridge this gap, enabling farmers to confidently use new technologies.
Managing Costs and Finding Funding
Cost concerns can be addressed through various approaches, including grants, cost-sharing programs, and cooperative purchasing. Implementing technology in phases can also help manage initial costs.
Dealing with Connectivity Issues
Connectivity challenges remain prevalent in many rural areas. Solutions such as offline-capable applications and low-bandwidth alternatives can help mitigate these issues, ensuring that technology remains accessible.
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Limited Digital Literacy | Digital Skills Training |
| High Initial Costs | Grants, Cost-Sharing Programs |
| Poor Internet Connectivity | Offline-Capable Applications |

By understanding these challenges and implementing effective solutions, farmers can successfully integrate technology into their traditional farming practices, enhancing productivity and sustainability.
Training and Support: Keys to Successful Adoption
The key to successful technology adoption lies in comprehensive training and ongoing support. Farmers and their workers need to be equipped with the knowledge and skills to effectively use new technology and tools.
Effective Training Strategies for Farm Workers
Effective training must be tailored to the specific audience, considering factors like existing knowledge levels, learning preferences, and cultural contexts. Some key strategies include:
- Hands-on, practical training approaches that yield better results than theoretical instruction.
- Ongoing training rather than a one-time event, with regular refresher sessions.
- Using storytelling and relatable analogies to explain complex concepts, such as comparing data flows to water canals.
Building a Support Network
Farmers benefit from building a support network that connects them with peers who are using similar tech and technology. This network enables knowledge sharing and collaborative problem-solving. Technical support resources should be readily accessible and responsive to farmers’ needs.

Case Studies: Successful Technology Integration on Traditional Farms
Technology is revolutionizing the agricultural sector, with numerous success stories emerging from traditional farms. The integration of modern technology with age-old farming practices is leading to improved productivity, efficiency, and sustainability.
Small-Scale Farm Success Stories
Several small-scale farms have achieved significant success through the adoption of technology. For instance, a mobile-based tracking system helped a farm boost its cassava yield by 20% and reduce spoilage. Simple, user-friendly technologies like SMS-based systems have proven to be particularly effective in these contexts.
| Technology | Impact | Lesson Learned |
|---|---|---|
| Mobile-based tracking | 20% boost in cassava yield, reduced spoilage | Simplicity + SMS = success |
| AI + crop rotation | Higher productivity without pesticides | Mix tradition (rotation) with precision (AI) |
| Drones repurposed from fishing gear | Accurate planting, reduced waste | Tech training via YouTube = unexpected innovation |
Lessons Learned from Implementation
The success stories highlight key lessons for successful technology integration. These include the importance of local adaptation, user-centered design, and incremental change. By embracing these principles, farmers can overcome common challenges like limited resources and connectivity issues.

Balancing Tradition and Innovation: Preserving Farming Heritage
Preserving the essence of traditional farming while embracing technology is vital for sustainable agriculture.
To achieve this balance, it’s essential to honor traditional knowledge while integrating modern innovations. Traditional farming knowledge represents generations of careful observation and adaptation, remaining valuable even as technology advances.
Honoring Traditional Knowledge
The most successful technology integration approaches honor this heritage by documenting traditional practices and incorporating their wisdom into new systems.
Creating a Hybrid Approach
Creating hybrid approaches means identifying which aspects of farming should be preserved and which can be enhanced through technological innovation. This balanced approach ensures that cultural knowledge continues to evolve.
Conclusion: The Future of Integrated Farming
Farming is on the cusp of a revolution, driven by the thoughtful integration of traditional practices and modern technology. The future of agriculture depends on balancing traditional wisdom with innovative tools like advanced IoT devices and precision farming techniques.
Emerging technologies will continue to expand possibilities for farms of all sizes, improving yields and reducing costs. Successful farmers will maintain a learning mindset, evaluating new tools while preserving valuable traditional practices. The goal remains creating farming systems that are productive, profitable, environmentally sustainable, and culturally appropriate.
FAQ
What are the primary benefits of using IoT devices in farming?
IoT devices and smart sensors can help farmers monitor and manage their crops more effectively, leading to increased productivity and yields. They provide real-time data on soil moisture, temperature, and crop health, enabling precision agriculture techniques.
How can mobile applications improve farm management?
Mobile applications and farm management software can help farmers streamline their operations, track expenses, and make data-driven decisions. They can also provide insights into weather patterns, allowing for more informed decisions about planting and harvesting.
What is precision irrigation, and how can it benefit farmers?
Precision irrigation involves using advanced technologies, such as sensors and drones, to optimize water usage. This can help reduce waste, lower costs, and promote sustainable farming practices.
Can drones be used for crop monitoring, and what are the benefits?
Yes, drones equipped with cameras and sensors can be used for crop monitoring, providing valuable insights into crop health, growth, and development. This can help farmers identify issues early, reducing the risk of crop failure and improving yields.
How can blockchain technology be used in agriculture?
Blockchain technology can be used to promote supply chain transparency, enabling consumers to track the origin and movement of produce. This can help build trust and promote fair trade practices.
What are the challenges of implementing new technologies on traditional farms?
Some of the challenges include addressing digital literacy gaps, managing costs, and dealing with connectivity issues. Providing effective training and support can help overcome these challenges.
How can farmers balance tradition with innovation?
By embracing a hybrid approach that combines traditional knowledge with modern technologies, farmers can preserve their heritage while improving productivity and sustainability.
What are the economic benefits of adopting new technologies in farming?
Adopting new technologies can help farmers reduce costs, improve yields, and increase their competitiveness in the market, leading to economic advantages.